Physiotherapy V/S Medication: Best way to treat Muscular Pain?
Treating musculoskeletal pain usually involves a combination of physiotherapy and medications tailored to the specific cause and severity of the pain. Here’s an overview of both approaches:
1. Physiotherapy
- Manual Therapy:- Techniques like joint mobilization, soft tissue massage, and manipulation to improve movement and reduce pain.
- Stretching and Strengthening Exercises:- Helps improve flexibility, muscle strength, and support joints. It PREVENTS recurrence and promotes recovery.
- Postural Training:- Corrects posture, especially if pain is related to poor biomechanics or ergonomics.
- Heat and Cold Therapy:- To reduce inflammation and ease muscle tension.
- Ultrasound or Electrotherapy:- Can stimulate tissue healing and provide pain relief in certain conditions.
- Hydrotherapy:- Exercising in water can be beneficial, especially for those with arthritis or joint pain.
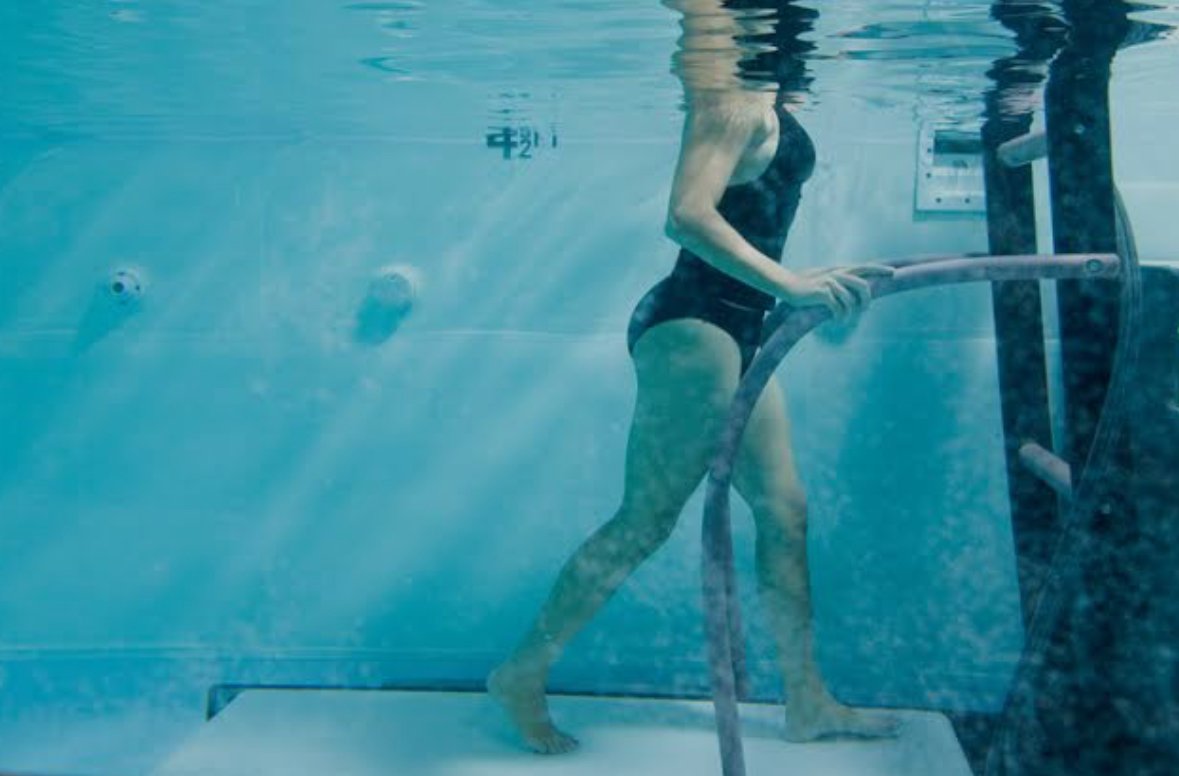
2. Medications
- Prescription Drugs Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: frequently used (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen) to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Analgesics:- Simple pain relievers like acetaminophen (paracetamol) may be recommended for milder pain.
- Muscle Relaxants:- To ease muscle spasms that can contribute to musculoskeletal pain.
- Corticosteroids:- To treat severe inflammation, corticosteroid injections are sometimes utilized.
- Topical Analgesics:- Creams or gels containing NSAIDs or capsaicin can provide localized pain relief.
- Antidepressants or Anticonvulsants:- For chronic pain management, especially if nerve involvement is suspected (e.g., fibromyalgia).a. Activity Modification
3. COMBINE THERAPY
- Resting:- Short-term rest may be advised after an acute injury, but too much rest can lead to stiffness and weakness. A balance between rest and activity is key.
- Gradual Resumption of Activity:- After recovery, it’s essential to gradually increase activity levels to avoid re-injury. Therapists will often guide you in this process.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):-It’s critical to treat the psychological aspect of pain when it’s persistent. Treating the psychological aspect of PAIN is crucial in cases of “CRONIC PAIN“. CBT can assist patients in managing their PAIN more effectively and in lowering the ‘STRESS’ and ‘ANXIETY’ brought on by chronic suffering. Pain perception is a crucial factor in illnesses like fibromyalgia and chronic back pain, thus mindfulness and relaxation techniques are beneficial in reducing pain.
4. When to See a Doctor
- Persistent Pain:- If pain lasts for more than a few weeks or worsens, it’s important to seek medical attention.
- Severe Pain or Trauma:- Sudden or sharp pain after an injury or fall, particularly if accompanied by swelling or inability to move the affected area, requires immediate medical evaluation.
- Chronic Conditions:- Conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or fibromyalgia need ongoing management and regular follow-ups with a healthcare professional.:-
Conclusion
- Personalised care is crucial since different pains require different remedies.Working together with doctors, physical therapists, and pain managers, among other medical professionals, guarantees a customised strategy that optimises healing and quality of life.