Fractures and its physiotherapy treatment
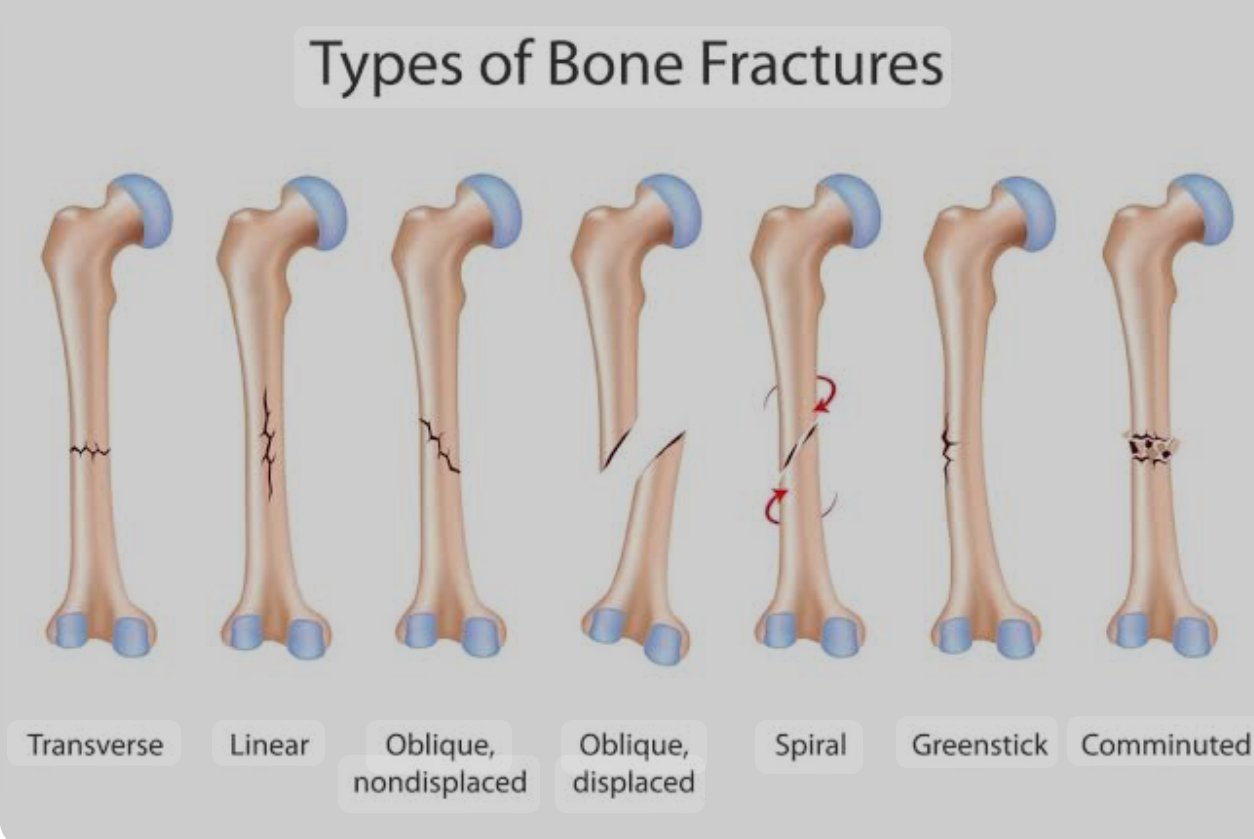
A fracture is a break or crack in a bone, typically resulting from trauma, overuse, or underlying conditions that weaken the bone, such as osteoporosis. Fractures can vary in severity and type, including simple (closed), compound (open), comminuted (where the bone is shattered into pieces), and others.
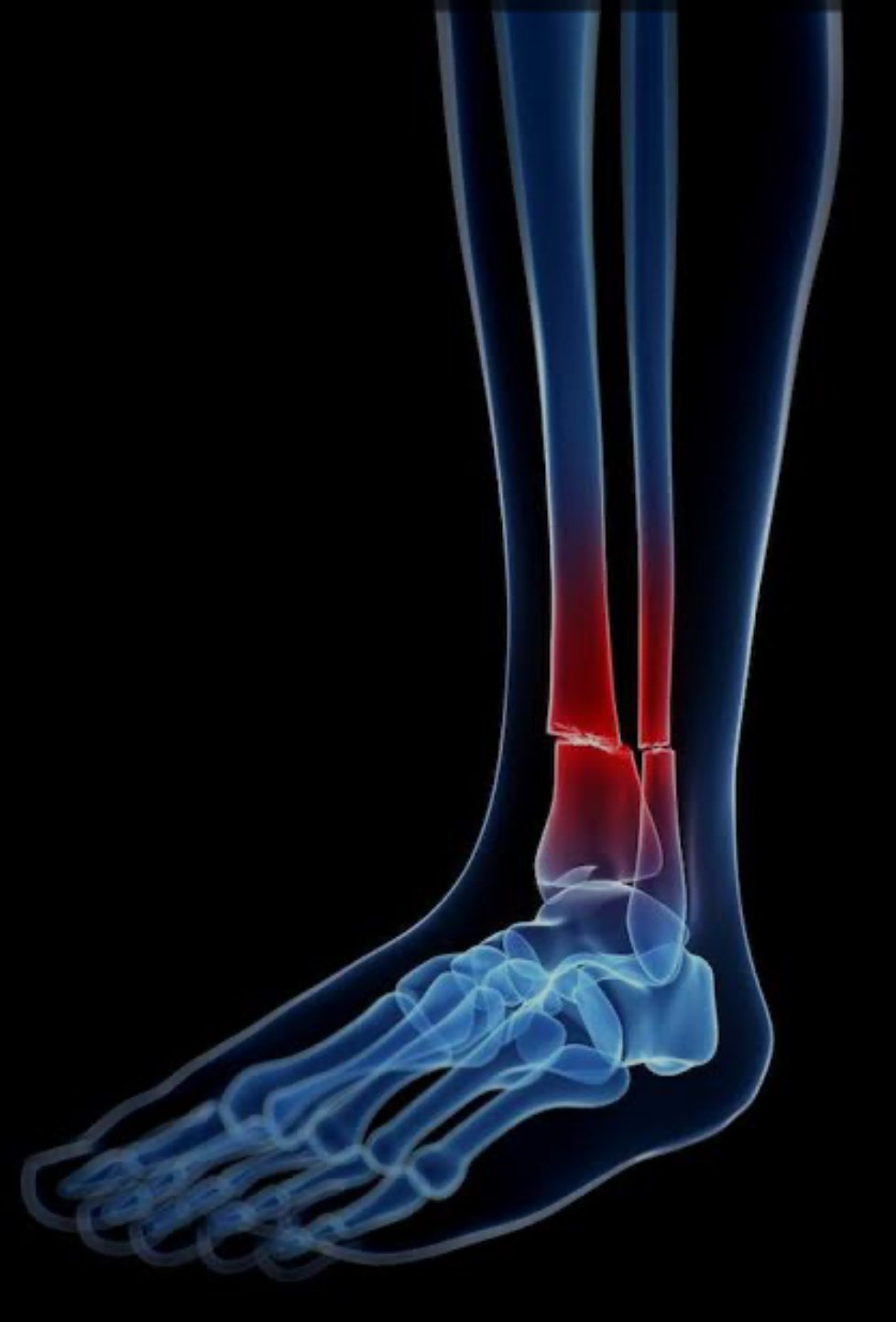
Types of Fracture
Goals

Physiotherapy Treatment for Fractures

Physiotherapy Treatment for Fractures
The healing and rehabilitation process after a fracture depends heavily on physiotherapy.. Restoring mobility, strength, and function as well as preventing problems and accelerating the healing process are the objectives of physical therapy.. Here’s an overview of the physiotherapy treatment for fractures:
- Initial Stage (Immobilization Phase):
- Immobilization: The affected limb is often immobilized using a cast, splint, or brace to allow the bone to heal properly.
- Pain Management: Physiotherapists may use modalities such as ice, heat, or electrical stimulation to manage pain and swelling.
- Maintaining Range of Motion (ROM): While the fractured area is immobilized, physiotherapy may focus on maintaining the ROM of adjacent joints (e.g., if the arm is in a cast, exercises for the shoulder and fingers may be prescribed).
- Gentle Isometric Exercises: Isometric contractions (muscle tightening without joint movement) might be encouraged to prevent muscle atrophy.
- Post-Immobilization Phase:
- Gradual Weight-Bearing: If the fracture was in a weight-bearing bone (e.g., leg), the physiotherapist will guide you on how to gradually start bearing weight on the affected limb.
- Joint Mobilization: Gentle joint mobilization techniques are used to restore normal joint function.
- Active and Passive ROM Exercises: These exercises help to regain the full range of motion of the affected joint.
- Soft Tissue Massage: This may be used to reduce stiffness and promote circulation.
- Strengthening Phase:
- Strengthening Exercises: Once the bone starts to heal and can tolerate more stress, strengthening exercises are introduced to rebuild muscle strength around the injured area.
- Proprioception and Balance Training: Exercises to improve balance and proprioception (awareness of the position and movement of the body) are important, especially for fractures in the lower limbs.
- Functional Rehabilitation:
- Functional Exercises: These exercises are designed to restore the ability to perform daily activities and sports-specific movements.
- Gait Training: If the fracture affected the leg, gait training might be necessary to restore normal walking patterns.
- Return to Normal Activities:Gradual Return to Activities: Physiotherapists will guide a gradual return to normal activities, work, and sports to avoid re-injury.
- Education: Patients are educated on injury prevention, proper body mechanics, and safe ways to resume activities.
Considerations
- Healing Time: The healing time varies depending on the type and location of the fracture, as well as the patient’s overall health.
- Patient Compliance: Adherence to the physiotherapy program is crucial for optimal recovery.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-ups with the physiotherapist are essential to monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Patients can regain full function and lower their chance of LONG -TERM issues with the help of this technique, which guarantees a safe and efficient recovery.