Low Back Pain A New Epidemic
Low back pain” is indeed becoming a significant concern in modern society. Factors contributing to this trend include prolonged sitting, poor posture, lack of physical activity, and increased stress.
The prevalence of low back pain has increased due to sedentary lifestyles and heavy reliance on technology, which often involves sitting for extended periods.
Addressing this issue involves promoting better ergonomics, regular exercise, and stretching, as well as adopting healthier lifestyle habits.
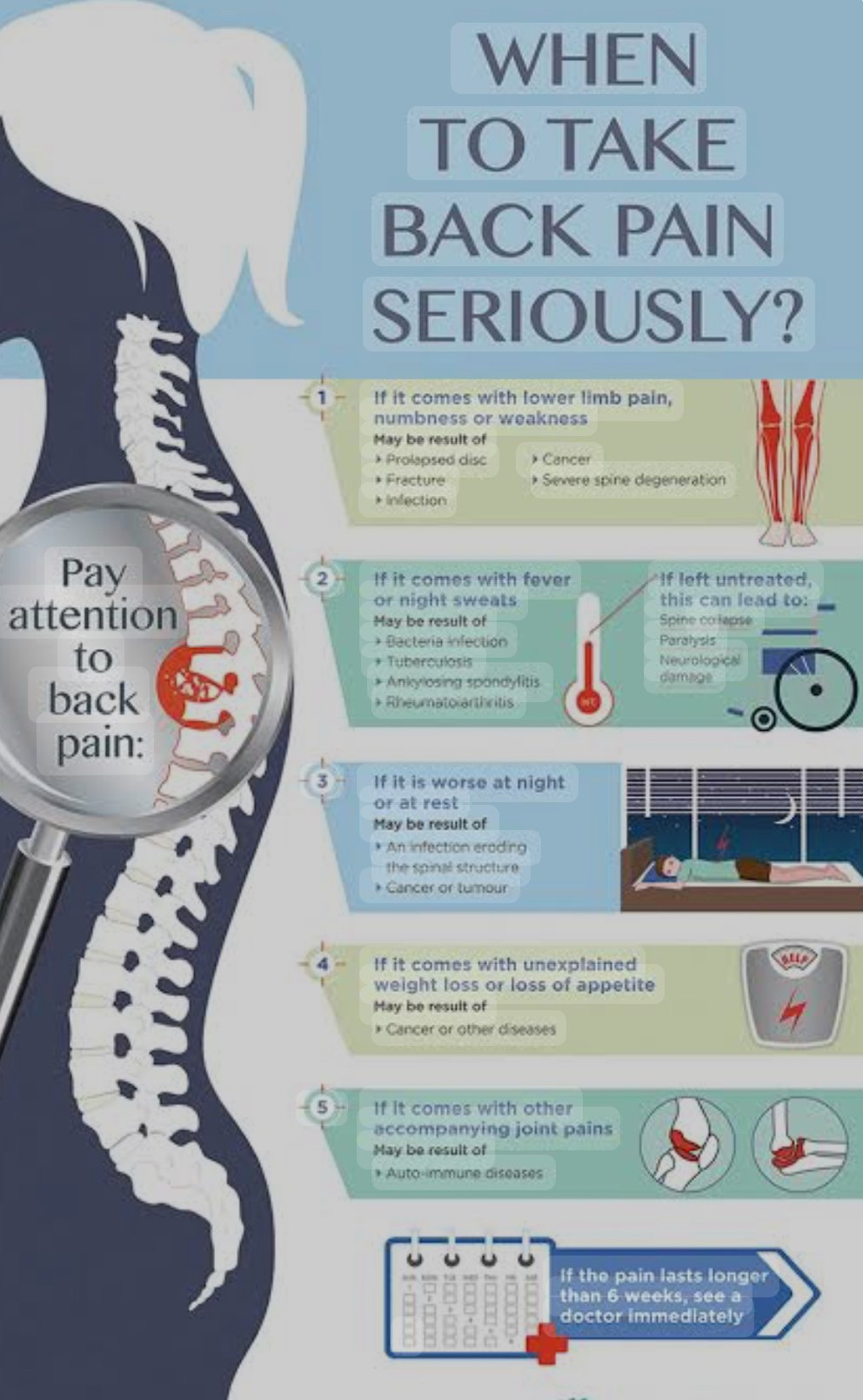
If you’re experiencing persistent pain, consulting a healthcare professional for an individualised assessment and treatment plan is advisable.
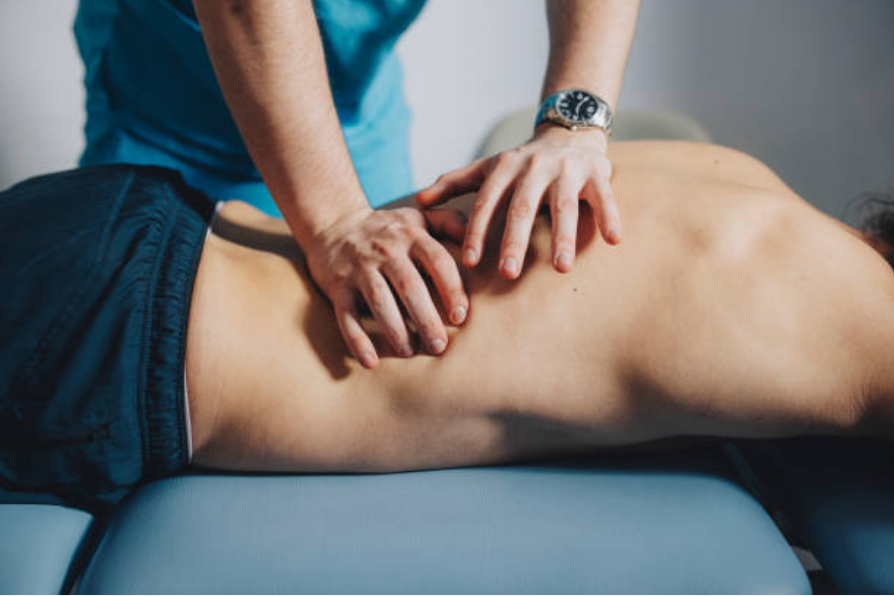
Contributing Factors

Contributing Factors
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Prolonged sitting, especially with poor posture, places undue stress on the lower back. Office workers and individuals who spend extended periods in front of screens are particularly affected.
- Poor Ergonomics: Improper desk setup, inadequate chair support, and incorrect screen positioning can lead to back strain.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Weak muscles and poor flexibility from insufficient exercise can contribute to back pain. Core strength, in particular, supports the spine and prevents strain.
- Obesity: Excess weight increases stress on the spine and surrounding muscles, contributing to pain.
- Injury and Overuse: Repetitive strain from lifting heavy objects improperly or engaging in strenuous activities can lead to back injuries.
- Aging: Age-related changes such as degenerative disc disease and spinal stenosis can contribute to back pain.
- Mental Health: Stress, anxiety, and depression can exacerbate or contribute to the perception of pain.
Consequences
- Reduced Quality of Life: Chronic back pain can limit daily activities, reduce mobility, and impair overall quality of life.
- Economic Impact: It leads to increased healthcare costs and lost productivity due to time off work.
- Physical and Psychological Effects: Persistent pain can lead to muscle atrophy, decreased physical fitness, and emotional issues like anxiety and depression.
Management and Prevention
- Exercise and Stretching: Frequent exercise, such as exercises for flexibility and core strength, can both prevent and treat back discomfort.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Ensuring a proper workstation setup, using supportive chairs, and maintaining good posture can help reduce back strain.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can decrease the load on the spine.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: Using correct lifting techniques—bending at the knees and keeping the back straight—can prevent injuries.
- Medical Treatment: For persistent or severe cases, physical therapy, medications, or even surgical options might be necessary.
- Mental Health Support: Addressing stress and mental health issues through counseling or relaxation techniques can help manage pain.
Emerging Trends
- Technology Integration: Wearable technology and apps that promote better posture and track physical activity are becoming more common.
- Preventive Health Programs: Preventive interventions like ergonomic training and wellness initiatives are being prioritized more and more by healthcare professionals and workplaces.
A multimodal strategy is required to address low back pain, including alterations in lifestyle, ergonomic modifications, and, if required, medical intervention.
Role of physiotherapy!!
PHYSIOTHERAPY can be highly effective in managing and controlling low back pain. Here’s how physiotherapists typically address this condition:
1. Assessment and Diagnosis
- Initial Evaluation: The physiotherapist will perform a thorough assessment, including reviewing medical history, performing physical examinations, and identifying movement limitations or pain triggers.
- Diagnosis: Based on the evaluation, the physiotherapist will diagnose the underlying causes of the pain and develop a targeted treatment plan.
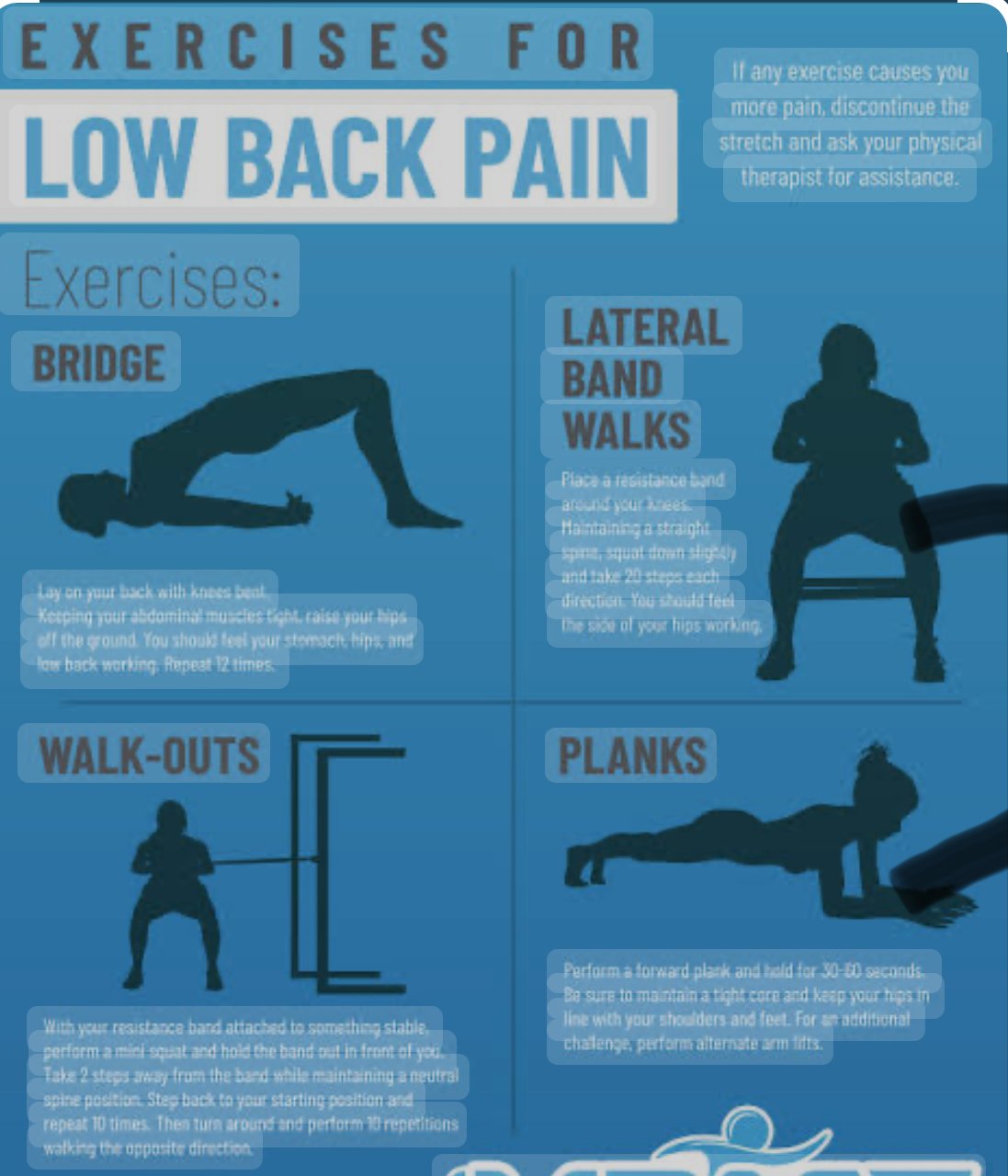
2. Exercise Therapy
- Strengthening Exercises: Focus on building strength in the core muscles (abdominals, obliques, and lower back muscles) to support and stabilise the spine.
- Flexibility Exercises: Stretching exercises improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension in the back and surrounding areas.
- Aerobic Conditioning: Low-impact aerobic exercises like walking or swimming can enhance overall fitness and support back health.

3. Manual Therapy
- Joint Mobilisation: Gentle, controlled movements to improve joint function and reduce pain.
- Soft Tissue Mobilisation: Techniques like massage to alleviate muscle tension, reduce stiffness, and improve circulation.
4. Posture and Ergonomics
- Postural Training: Guidance on maintaining proper posture while sitting, standing, and lifting to minimize strain on the back.
- Ergonomic Advice: Recommendations for adjusting workstations and daily activities to promote spinal health.
5. Pain Management Techniques
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Application of heat or cold packs to reduce inflammation and ease muscle pain.
- Electrotherapy: Use of modalities like TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) to manage pain and improve muscle function.
6. Education and Lifestyle Modifications
- Self-Care Strategies: Instruction on proper body mechanics, such as lifting techniques and safe movement practices.
- Lifestyle Advice: Encouragement to adopt healthy habits like regular physical activity, weight management, and stress reduction techniques.
7. Functional Training
- Activity Modification: Teaching patients how to modify activities or movements to avoid exacerbating the pain.
- Functional Exercises: Exercises tailored to improve the ability to perform daily tasks and activities more comfortably.
8. Progress Monitoring and Adjustment
- Regular Follow-Ups: Ongoing assessments to monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
- Feedback and Reassessment: Continuous evaluation of the effectiveness of the treatment and making modifications based on patient feedback and progress.
Physiotherapy can increase function, lower low back discomfort, and improve overall quality of life by utilising these techniques.For personalised treatment, consulting a licensed physiotherapist is essential.Low Back Pain A New Epidemic
